Good news, frequent flyers: Wi-Fi in the friendly skies could soon be less of a joke. It might even be good. Really good, potentially up to 20 times faster.
That is if all systems are go for Gogo’s fancy, new in-flight Internet system. The leading airborne Wi-Fi connectivity provider announced this week that the FAA has given it the greenlight to test its 2Ku connectivity tech, which it claims performs at speeds as fast as 70 megabits per second (Mbps). That’s exponentially speedier than Gogo’s most commonly used data signal bandwidth, which tops out at a frustratingly slow 3.1 Mbps, slower than the slowest home broadband signal.
Gogo’s current airborne Wi-Fi is inefficiently delivered via spotty air-to-ground cellular signals. The new, hopefully dramatically improved system uses twin, 4.5-inch tall satellite antennas. Basically, the signals they send and receive from satellites in orbit are more powerful and cleaner and crisper, which Gogo says means “more bandwidth at less cost.” Hmm, at less cost to whom? Probably not to passengers, but we’ll get to that in a minute.
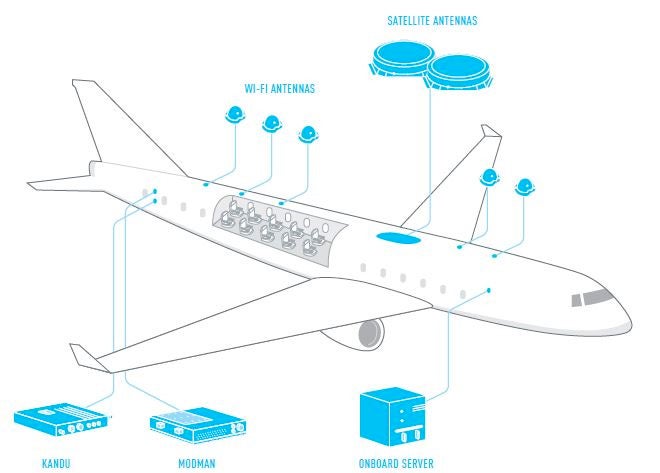
“This is a significant milestone for Gogo and a seminal event for in-flight Internet,” Gogo chief technology officer Anand Chari said in a statement. “We believe this will be the best performing technology for the global commercial aviation market bar none. Clearing this regulatory hurdle brings us one step closer to enabling our airline partners and their passengers to enjoy the future of in-flight Internet.”
The Chicago-based company’s new system is currently installed on its 737-500 test plane, where in-flight trials will take off shortly. Seven commercial airlines are already signed up “for either a trial or fleet deployment” of the advanced technology, including Brazil’s GOL Airlines and Delta Airlines, reports Avionics Magazine. Gogo expects to officially launch its next-gen system later this year, with rollout likely continuing through 2016.
Better stash your cash, passengers. We’re guessing Gogo’s faster Wi-Fi packages to come will probably be even pricier than its current offerings, which start at $16 for a full day of airborne connectivity. Satisfying the need for speed doesn’t come cheap at 45,000 feet.
